MetaMask is a non-custodial wallet, which means your keys stay with you, not on a company server. You have full control, but your security depends on how careful you are.
The wallet cannot see your funds, freeze them, or intervene if something goes wrong. With over 100 million users, it has been tested widely, is open source, audited, and supported by ConsenSys.
Most losses happen due to user mistakes, not MetaMask itself. This article explains how MetaMask keeps your crypto safe, its limits, and simple steps you can take to boost your security.
Is MetaMask Safe: Key Takeaways
- MetaMask can be secure when used properly, but because it is non-custodial, security really sits with the user.
- A hardware wallet lowers risk by keeping assets offline, and audited open-source code adds another layer of protection.
- The 12-word Secret Recovery Phrase is the master key and must stay offline and private.
- Transactions cannot be reversed, lost funds are gone for good, and after a scam, the move is to report it and shift any remaining assets to a new secure wallet.
- Most real-world losses happen on the user side, with phishing leading the way and malware close behind.
What Makes MetaMask Safe
MetaMask relies on layered defenses that target different failure points. Some protect the code itself, others focus on transactions, and many are designed to catch user mistakes before funds move.
Key Storage and Self-Custody
- MetaMask is self-custodial, with private keys and recovery phrases that are created and encrypted locally on your device. They are never sent to MetaMask servers.
- MetaMask cannot see your funds, freeze them, or step in—making your recovery phrase the most important thing you own.
- Social login option: Recovery phrase is split, encrypted, and stored across multiple nodes. Access requires a Google/Apple account + MetaMask password, reducing single points of failure.
Code Security: LavaMoat and Isolation
- LavaMoat isolates JavaScript dependencies to prevent a compromised library from taking over the wallet.
- Any malicious code that slips through is contained, protecting the rest of the wallet.
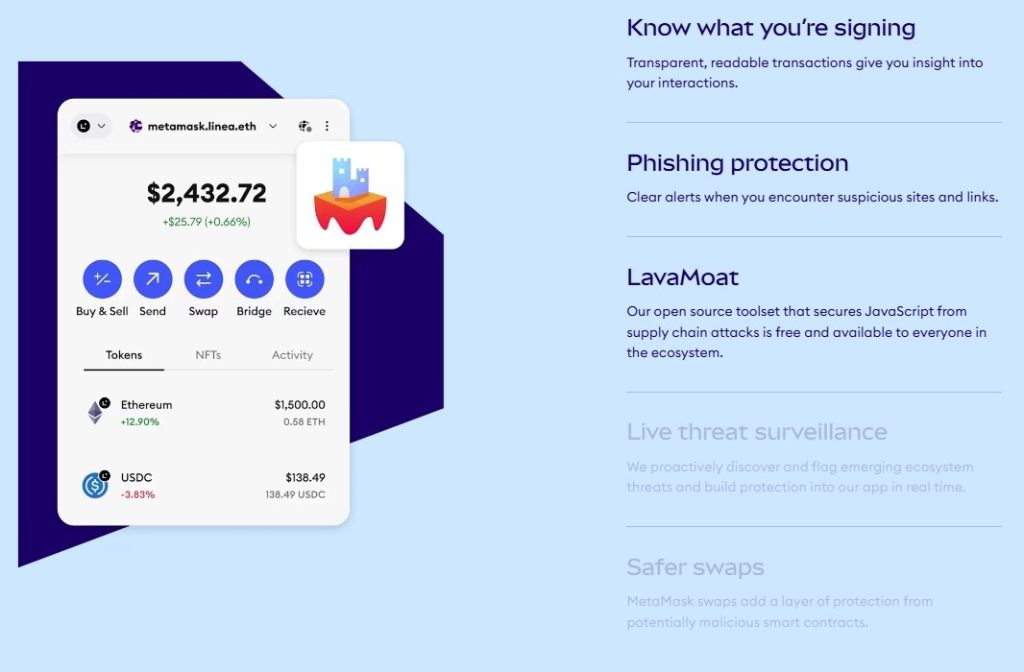
Transaction Safety
- Simulation and Scam Detection: Transactions are simulated with Blockaid before approval. Warnings appear for wallet drains, malicious approvals, or known scams.
- Human-readable transaction warnings: Shows contract permissions, spending limits, and unlimited access requests to prevent mistakes.
Phishing and Malicious Site Protection
- Eth Phishing Detect blocks known scam domains and stops connections to phishing sites.
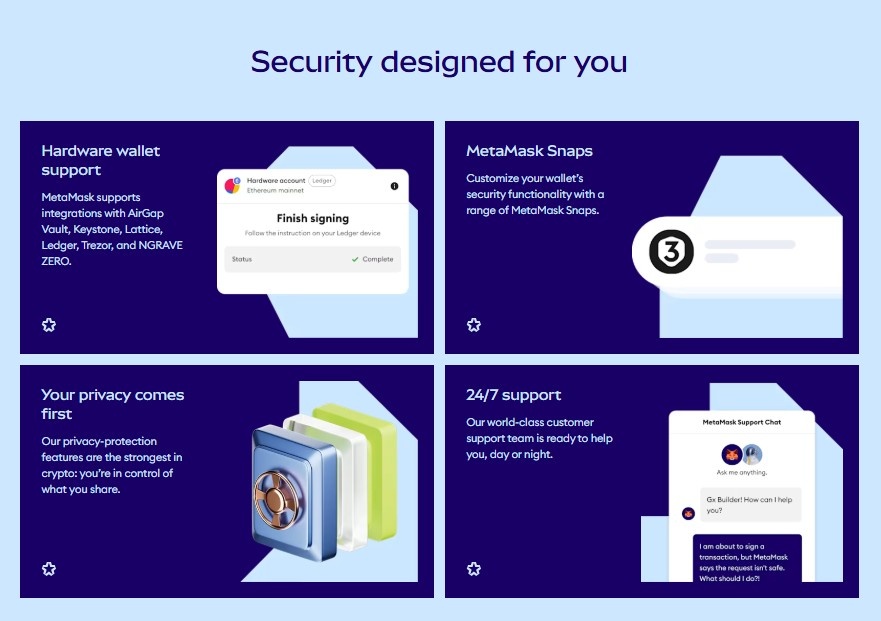
Hardware Wallet Support
- Works with Ledger, Trezor, Keystone, and Lattice.
- Private keys stay on the device; every transaction requires a physical button press, adding extra security.
Permission Management
- Users can review and revoke token approvals, limit unlimited approvals, and set spending caps to reduce risk from malicious dApps.
Open Source, Audits, and Bug Bounties
- Open source code allows inspection by anyone.
- Security firms audit MetaMask, and bug bounty programs reward researchers for finding vulnerabilities.
Updates and Active Defense
- Regular updates respond to new threats like address poisoning, fake NFT mints, and search engine phishing.
- Keeping MetaMask updated ensures your defenses remain strong.
MetaMask Risk Management
MetaMask includes several safeguards that make everyday crypto use reasonably safe, but that safety has limits.
It reduces exposure; it does not eliminate risk. Here is a brief look at MetaMask’s risk management method.
- Built for risk reduction, not immunity: Problems tied to user behavior still slip through. Compromised devices, fake NFT links, phishing sites, or careless clicks sit outside the wallet’s control. The software can help, but it cannot supervise you.
- Open source and publicly scrutinized: One of MetaMask’s biggest strengths is that its code is open source. Anyone can inspect it.
That invites formal audits and constant informal review by developers who are quick to flag weaknesses. - Forced confirmation on every action: MetaMask requires manual approval for every transaction. Details are shown clearly before anything is signed.
This friction can feel annoying, but it often stops accidental approvals, especially when a request suddenly asks for broader permissions than expected. - Hardware wallet support: By supporting hardware wallets like Ledger and Trezor, MetaMask lets private keys stay offline while still offering browser-level convenience. This setup significantly lowers risk without killing usability.
- Updates matter more than people think: Regular updates patch bugs and respond to new attack methods. Skipping them quietly weakens protections already in place.
MetaMask also publishes monthly security reports that track active threats across the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
These reports are not audits of the wallet itself. Instead, they document real incidents, scam patterns, and attack methods that users are most likely to encounter.
The December 2025 MetaMask Crypto Security Report highlights how modern attacks increasingly target people rather than software.
It details North Korea–linked job scams aimed at infiltrating crypto companies, large-scale money laundering operations using stablecoins, and major exploits such as the Balancer liquidity pool attack that forced a network halt.
Risks Associated With Using MetaMask
Even with the precautions that MetaMask implements, it would be unrealistic to consider it entirely secure.
Due to its role as a hot wallet, always online, it is directly susceptible to phishing attacks, malware, and specific hacking efforts.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing is the most common way MetaMask users lose funds. Fake websites and browser extensions look real and trick users into entering their seed phrase.
- Device Malware: On infected devices, malware can steal passwords or keys in the background. Some even change wallet addresses during a transaction, sending funds to the wrong place.
- Social Engineering Scams: Fraudsters often impersonate MetaMask support personnel or agents from reputable cryptocurrency projects, contacting users via email, social media, or chat services.
The strategy is straightforward yet powerful. The attack succeeds due to the manipulation of trust rather than the compromise of software. - User Error: Simple mistakes cause as much damage as real attacks. Seed phrases get misplaced, shared casually, or stored as screenshots and cloud backups that seem convenient but quietly increase risk.
- Smart Contract Risks: Smart contracts introduce a quieter kind of danger. Connecting to a malicious dApp or approving unlimited token access can drain funds without obvious warnings or immediate signs of trouble.
Best Practices For Using MetaMask Safely
The habits below are not dramatic, but in practice, they are what separate routine use from avoidable mistakes.

- Use a long, unique password and never reuse old ones from other sites.
- Store your recovery phrase offline on paper or metal and keep it away from anything digital.
- Never share your recovery phrase because no real support or project will ever ask for it.
- For larger balances, use MetaMask with a hardware wallet like Ledger or Trezor.
- Only connect your wallet to official websites and avoid rushed clicks on lookalike pages.
- Slow down before approving transactions, and do not accept unlimited token approvals casually.
- Keep MetaMask, your browser, and extensions updated from official sources only.
- Use a separate browser profile for cryptocurrency activity if possible.
- Protect related accounts with two-factor authentication and stay alert to fake urgency or support messages.
Comparison of MetaMask To Other Wallets
The comparison below analyzes how various wallet types measure up in relation to several key features.
The goal is not to identify a singular victor, but to provide users with a better understanding of which choice corresponds most closely with their intended use of cryptocurrency.
| Parameter | MetaMask | Hardware Wallet(Ledger/Trezor) | Mobile Wallet(Trust Wallet/Exodus) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Level | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Private Key Storage | Stored encrypted on the device | Stored offline in a device | Stored on phone |
| Ease of Use | Beginner friendly | Medium, requires device setup | Easy, mobile-focused |
| Best For | DApps, NFTs, and everyday use | Long-term storage, large holdings | General users, mobile-first |
| Browser/DApp Integration | Excellent | Good (when connected via MetaMask) | Limited or app-dependent |
| Cost | Free | Paid($60-$200) | Free |
| Recovery Method | 12-word seed phrase | 24-word seed phrase | Seed phrase |
| Supported Network | Ethereum + EVM chains | Depends on the model, supports many | Many(varies by wallet ) |
Related Reads:
Conclusion: MetaMask Is Generally Safe If Used Correctly
MetaMask is generally safe, but it is not a set-and-forget wallet. It gives you control, not protection by default.
Its real strength comes from self-custody, layered safeguards, and those constant confirmation prompts that force you to slow down.
When you store recovery phrases offline, double-check permissions, and pair them with a hardware wallet, MetaMask works well for everyday cryptocurrency use.
But cut corners and things break fast. There is no safety net. MetaMask reduces risk, but it never replaces awareness, discipline, or common sense.
FAQs
For most people, yes. When it’s used properly, it’s considered safe. Your private keys stay on your device, not on MetaMask’s servers, so control stays with you.
Usually, the wallet isn’t the problem. Losses tend to come from phishing links, fake sites, malware, or people sharing their seed phrase without realizing what they’re doing.
Then the wallet is gone. There’s no reset button. MetaMask can’t recover it for you.
It doesn’t store your keys or recovery phrase. Some basic network data can still pass through default providers, unless you change those settings yourself.
Stop. Don’t sign anything. Close the page. Check the URL. If needed, move funds before doing anything else.
Yes. You can restore the same wallet anywhere using the same seed phrase.
Transactions can’t be reversed. Move what’s left, revoke approvals, and report it. MetaMask can’t undo it.


